Methods in Design Science Research
Design Science Research is a broad research paradigm that aims to generate design knowledge. There are a number of different methodological approaches that can find their application in DSR. In this blog post, three relevant methods are presented.
 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashDesign Science Research aims to generate prescriptive knowledge about the design of artifacts, such as software, methods, models or concepts. This design knowledge helps research and practice to design artifacts systematically and scientifically in future projects. This design and application can in turn generate design-oriented knowledge that contributes to a DSR knowledge corpus (Hevner et al. 2004).
In order to contribute to both theory and practice of solving real-world problems, it is necessary not only to design novel solutions (artifacts), but also to demonstrate its broad impact on the application domain. This is to demonstrate the so-called rigor and relevance of DSR. DSR thus seeks to generate knowledge on how to effectively design and deploy novel solutions to relevant problems. The knowledge that is generated must include information about the solution, but also evidence that shows how well the novel solution addresses the problem. Thus, it should be shown how the solution can be effectively used in the real world to satisfy the needs of the stakeholders dealing with the problem (vom Brocke et al. 2020).
This knowledge covers three fundamental aspects in DSR; the problem space and the solution space. In addition, there is the knowledge that describes the effectiveness of the problem solution through the generated artifact(s), which is called the evaluation. The evaluation describes to what extent the constructed novel artifacts (solution space) address the problem space and satisfy the stakeholders of the problem. The following diagram shows these three relevant aspects of design-oriented knowledge.
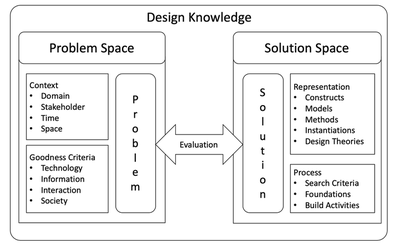
All aspects contribute to the overall DSR knowledge corpus and are elaborated and evaluated in a systematic way within a DSR project. To ensure that this knowledge is elaborated in a comprehensible (e.g. empirical) way, various (scientific) methods are used in the DSR, which are discussed below.
Systematic literature reviews
Systematic literature reviews (systematic literature reviews) create a solid foundation for the generation of knowledge. They facilitate theory development and reveal areas where research is needed. They also serve in DSR to understand the problem space by identifying existing literature and highlighting areas to be explored. They also serve as a basis for shaping the solution space, for example, through the influence of relevant theories (kernel theories). A comprehensive DSR project should include a systematic literature review. Relevant literature on the method: Webster and Watson (2002) and vom Brocke et al. (2015).
Interviews
Interviews are considered an empirical research method to get mainly qualitative insights from, for example, experts in a certain field. They can be used to set requirements (meta requirements) for the solution space, which have a strong foundation to the problem space, if the interviewees are part of the problem’s stakeholder group. In this way, it can be ensured already during the creation of the artifact that the problem space is addressed as well as possible. For example, design principles can be generated from the results of interviews, which can be used to design artifacts. Furthermore, interviews are used to evaluate designed artifacts and thus refine or extend design knowledge. Relevant literature on the method: Mayring (2014).
Experiments
Experiments are a proven means to generate or validate design knowledge, especially due to their high internal validity. With experiments isolated aspects, such as the effectiveness of individual design principles can be evaluated, but also of individual functionalities, mechanisms or software features. The effectiveness of entire artifacts can also be demonstrated with the help of experiments, for example to achieve a generalization of design knowledge. Experiments are thus considered a powerful empirical tool to generate and evaluate design knowledge. Relevant literature on the method: large Deters et al. (2019) and Dennis and Valacich (2001).
Other Methods
In addition to these popular methods in DSR, other methods or combinations of different methods exist that are used to generate design knowledge. For example, taxonomies can be developed to create or classify design knowledge, such as design principles. A methodological approach for this was developed by Nickerson et al. (2013). Other methods are simulations, case studies, ethnography or the grounded theory approach.
Design Science Research is a broad research paradigm that aims to generate design knowledge. Consequently, a number of different methodological approaches exist on how the problem space can be systematically elaborated, how the solution space can be found and designed, but also how effectively the designed solution space addresses the problems to be addressed. In this article, three possible methods have been presented that are used in DSR.